Japan will ban vaccinated people from donating “tainted blood”, social media users are claiming.
This is false. There is no such proposal and the claim is based on a misrepresentation of a non peer-reviewed paper.
The claim is made in Facebook posts which share a screengrab of an article from a misinformation website headlined “Japan to ban vaccinated people from donating ‘tainted blood’.”
The claim is repeated in posts that all share the same article.
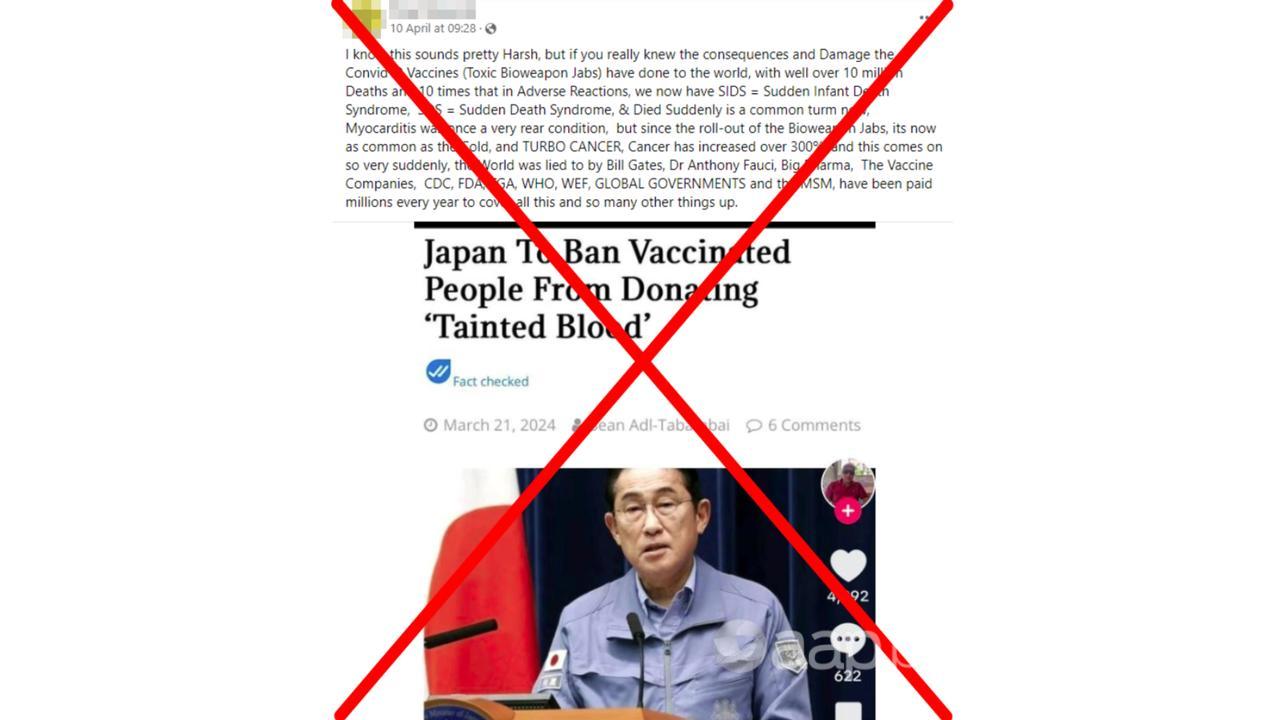
The March 21 article comes from The People’s Voice, a website known for publishing viral misinformation and fabricated clickbait news stories.
“Japan has proposed banning people who receive the COVID-19 vaccine from donating blood, due to the dangerous side effects of mRNA,” the article states.
“A team of top Japanese scientists have urged the government to immediately outlaw the COVID mRNA shots and prohibit anybody who has taken the vaccine from giving blood.”
None of the sources used by the article back up the main claim.
The article links to a preprint paper titled “Concerns regarding Transfusions of Blood Products Derived from Genetic Vaccine Recipients and Proposals for Specific Measures“.
Preprint means it has not been peer-reviewed or published in a scientific or medical journal.
There is nothing in the paper that supports the claim. The paper doesn’t even call for such a ban.
Instead, the authors argue the impact of the vaccines on blood products “are unknown at present.”
The paper calls for the vaccination program to be suspended while a harm-benefit assessment can be carried out on the impact on blood products.
Japanese public health expert Sharon Hanley, from Aberdeen University, said the authors of the preprint paper were not experts in vaccine safety.
“Since this is neither a published paper, nor a paper written by experts in the field, I think it is highly unlikely it would be on the government’s current list of things to consider.”
A spokesman for Japan’s Pharmaceutical Safety Bureau’s Blood and Blood Products Division confirmed to AAP FactCheck there is no ban on those who have received the vaccine.
He said there were some restrictions on blood collection after COVID-19 vaccination that were “considered as internationally and scientifically appropriate”.
The “restrictions” are time delays of 48 hours for blood collection after vaccination with mRNA vaccines, six weeks after virus vector vaccines, and 24 hours after recombinant protein vaccines.
The spokesman said it was not prohibited to manufacture or use blood products based on donated blood from people vaccinated against COVID-19.
The Verdict
The claim that Japan has proposed banning people who have received the COVID-19 vaccine from donating blood is false.
Japan’s Pharmaceutical Safety Bureau confirmed that there is no such proposed or actual ban.
The claim is based on the misrepresentation of a pre-print study.
False — The claim is inaccurate.
AAP FactCheck is an accredited member of the International Fact-Checking Network. To keep up with our latest fact checks, follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
All information, text and images included on the AAP Websites is for personal use only and may not be re-written, copied, re-sold or re-distributed, framed, linked, shared onto social media or otherwise used whether for compensation of any kind or not, unless you have the prior written permission of AAP. For more information, please refer to our standard terms and conditions.